# Copyright (c) Meta Platforms, Inc. and affiliates. All rights reserved.
本教程展示了cameras、transforms和so3 API。
我们处理的问题定义如下
给定一个包含$N$个相机的光学系统,其外部参数为$\{g_1, ..., g_N | g_i \in SE(3)\}$,以及一组相对相机位置$\{g_{ij} | g_{ij}\in SE(3)\}$,这些位置映射在随机选择的相机对$(i, j)$的坐标系之间,我们寻找与相对相机运动一致的绝对外部参数$\{g_1, ..., g_N\}$。
更正式地说:$$ g_1, ..., g_N = {\arg \min}_{g_1, ..., g_N} \sum_{g_{ij}} d(g_{ij}, g_i^{-1} g_j), $$, 其中$d(g_i, g_j)$是一个合适的度量,用于比较相机$g_i$和$g_j$的外部参数。
从视觉上看,问题可以描述如下。下图描绘了优化开始时的场景。真实相机以紫色绘制,而随机初始化的估计相机以橙色绘制: 
我们的优化旨在通过最小化相对相机对之间的差异,使估计(橙色)相机与真实(紫色)相机对齐。因此,问题的解决方案应如下所示: 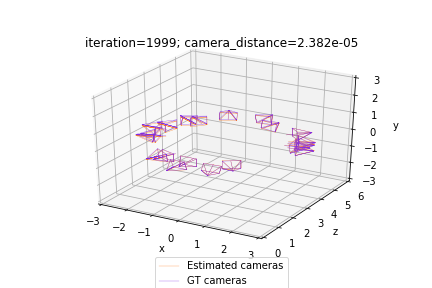
在实践中,相机外部参数$g_{ij}$和$g_i$使用SfMPerspectiveCameras类的对象表示,这些对象使用相应的旋转和平移矩阵R_absolute和T_absolute初始化,这些矩阵定义了外部参数$g = (R, T); R \in SO(3); T \in \mathbb{R}^3$。为了确保R_absolute是一个有效的旋转矩阵,我们使用旋转的轴角表示log_R_absolute的指数映射(用so3_exp_map实现)来表示它。
请注意,此问题的解决方案只能恢复到一个未知的全局刚性变换$g_{glob} \in SE(3)$。因此,为简单起见,我们假设已知第一个相机$g_0$的绝对外部参数。我们将$g_0$设置为一个平凡的相机$g_0 = (I, \vec{0})$。
确保已安装torch和torchvision。如果未安装pytorch3d,请使用以下单元格安装它
import os
import sys
import torch
need_pytorch3d=False
try:
import pytorch3d
except ModuleNotFoundError:
need_pytorch3d=True
if need_pytorch3d:
if torch.__version__.startswith("2.2.") and sys.platform.startswith("linux"):
# We try to install PyTorch3D via a released wheel.
pyt_version_str=torch.__version__.split("+")[0].replace(".", "")
version_str="".join([
f"py3{sys.version_info.minor}_cu",
torch.version.cuda.replace(".",""),
f"_pyt{pyt_version_str}"
])
!pip install fvcore iopath
!pip install --no-index --no-cache-dir pytorch3d -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/pytorch3d/packaging/wheels/{version_str}/download.html
else:
# We try to install PyTorch3D from source.
!pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d.git@stable'
# imports
import torch
from pytorch3d.transforms.so3 import (
so3_exp_map,
so3_relative_angle,
)
from pytorch3d.renderer.cameras import (
SfMPerspectiveCameras,
)
# add path for demo utils
import sys
import os
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(''))
# set for reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(42)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
print("WARNING: CPU only, this will be slow!")
如果使用Google Colab,请获取用于绘制相机场景的实用程序文件以及真实相机位置
!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d/main/docs/tutorials/utils/camera_visualization.py
from camera_visualization import plot_camera_scene
!mkdir data
!wget -P data https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d/main/docs/tutorials/data/camera_graph.pth
或者,如果本地运行,请取消注释并运行以下单元格
# from utils import plot_camera_scene
# load the SE3 graph of relative/absolute camera positions
camera_graph_file = './data/camera_graph.pth'
(R_absolute_gt, T_absolute_gt), \
(R_relative, T_relative), \
relative_edges = \
torch.load(camera_graph_file)
# create the relative cameras
cameras_relative = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = R_relative.to(device),
T = T_relative.to(device),
device = device,
)
# create the absolute ground truth cameras
cameras_absolute_gt = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = R_absolute_gt.to(device),
T = T_absolute_gt.to(device),
device = device,
)
# the number of absolute camera positions
N = R_absolute_gt.shape[0]
def calc_camera_distance(cam_1, cam_2):
"""
Calculates the divergence of a batch of pairs of cameras cam_1, cam_2.
The distance is composed of the cosine of the relative angle between
the rotation components of the camera extrinsics and the l2 distance
between the translation vectors.
"""
# rotation distance
R_distance = (1.-so3_relative_angle(cam_1.R, cam_2.R, cos_angle=True)).mean()
# translation distance
T_distance = ((cam_1.T - cam_2.T)**2).sum(1).mean()
# the final distance is the sum
return R_distance + T_distance
def get_relative_camera(cams, edges):
"""
For each pair of indices (i,j) in "edges" generate a camera
that maps from the coordinates of the camera cams[i] to
the coordinates of the camera cams[j]
"""
# first generate the world-to-view Transform3d objects of each
# camera pair (i, j) according to the edges argument
trans_i, trans_j = [
SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = cams.R[edges[:, i]],
T = cams.T[edges[:, i]],
device = device,
).get_world_to_view_transform()
for i in (0, 1)
]
# compose the relative transformation as g_i^{-1} g_j
trans_rel = trans_i.inverse().compose(trans_j)
# generate a camera from the relative transform
matrix_rel = trans_rel.get_matrix()
cams_relative = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = matrix_rel[:, :3, :3],
T = matrix_rel[:, 3, :3],
device = device,
)
return cams_relative
最后,我们开始优化绝对相机。
我们使用带动量的SGD,并对log_R_absolute和T_absolute进行优化。
如前所述,log_R_absolute是我们绝对相机的旋转部分的轴角表示。我们可以使用以下方法获得对应于log_R_absolute的3x3旋转矩阵R_absolute:
R_absolute = so3_exp_map(log_R_absolute)
# initialize the absolute log-rotations/translations with random entries
log_R_absolute_init = torch.randn(N, 3, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
T_absolute_init = torch.randn(N, 3, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
# furthermore, we know that the first camera is a trivial one
# (see the description above)
log_R_absolute_init[0, :] = 0.
T_absolute_init[0, :] = 0.
# instantiate a copy of the initialization of log_R / T
log_R_absolute = log_R_absolute_init.clone().detach()
log_R_absolute.requires_grad = True
T_absolute = T_absolute_init.clone().detach()
T_absolute.requires_grad = True
# the mask the specifies which cameras are going to be optimized
# (since we know the first camera is already correct,
# we only optimize over the 2nd-to-last cameras)
camera_mask = torch.ones(N, 1, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
camera_mask[0] = 0.
# init the optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD([log_R_absolute, T_absolute], lr=.1, momentum=0.9)
# run the optimization
n_iter = 2000 # fix the number of iterations
for it in range(n_iter):
# re-init the optimizer gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# compute the absolute camera rotations as
# an exponential map of the logarithms (=axis-angles)
# of the absolute rotations
R_absolute = so3_exp_map(log_R_absolute * camera_mask)
# get the current absolute cameras
cameras_absolute = SfMPerspectiveCameras(
R = R_absolute,
T = T_absolute * camera_mask,
device = device,
)
# compute the relative cameras as a composition of the absolute cameras
cameras_relative_composed = \
get_relative_camera(cameras_absolute, relative_edges)
# compare the composed cameras with the ground truth relative cameras
# camera_distance corresponds to $d$ from the description
camera_distance = \
calc_camera_distance(cameras_relative_composed, cameras_relative)
# our loss function is the camera_distance
camera_distance.backward()
# apply the gradients
optimizer.step()
# plot and print status message
if it % 200==0 or it==n_iter-1:
status = 'iteration=%3d; camera_distance=%1.3e' % (it, camera_distance)
plot_camera_scene(cameras_absolute, cameras_absolute_gt, status)
print('Optimization finished.')
在本教程中,我们学习了如何初始化一批SfM相机、为捆绑调整设置损失函数以及运行优化循环。